Print dies and an engraver’s View of Canada
The British American Bank Note Company head office and plant located at 975 Gladstone Ave., Ottawa. 1948–2012.
In 2012, BA International Inc., formerly known as the British American Bank Note Company (BABN), closed its doors on Gladstone Avenue in Ottawa, ending a tradition of security printing in Canada dating back to 1866. Founded in Montréal by George Burland and W.C. Smillie, BABN was one of Canada’s principal security printers, producing secure documents for government and commercial clients alike. Products included passports, bank notes, share certificates, bonds, stamps and lottery tickets to name but a few.
In May 2013, staff of the Bank of Canada Museum visited BABN and were able to select for the National Currency Collection more than 650 steel dies (small, engraved metal or “intaglio” plates) and other production tools formerly used by the company to prepare the intaglio printing plates. The group included machine etched borders or lathework and numerals or counters. But the bulk of the selection consisted of hand engraved images of landscapes and people. Most are quite small, measuring roughly four by three inches. These were the heart of the security printer’s trade.
Traditionally, the intaglio printing process put the “security” in security printing. Commercial printing techniques could not match exactly the tactile feel of raised ink transferred under pressure from steel plates incised with intricate and artistic designs.
We thank BA International and their parent company Giesecke & Devrient for their generous donation to the National Currency Collection. It is deeply appreciated. These tools are not only an important link to BABN and the many government and commercial contracts it handled in times of peace and adversity, but also a testament to the beauty of the engraver’s art. What’s more, they are a record of times past through which we catch glimpses of the march of time in Canada.
Die #134, “Forest Scene”. This note was issued by the Department of the Interior in 1876. Called land scrip, these instruments were used to purchase land in the newly opened areas of western Canada. (NCC 2013.29.116) and (NCC 1977.180.1)
Die #482#2 shows a man in the fields on the back of a horse-drawn reaper-binder. Developed in the 1870s the reaper-binder cut wheat and tied it into bundles, freeing farm labour for other activities. (NCC 2013.29.412)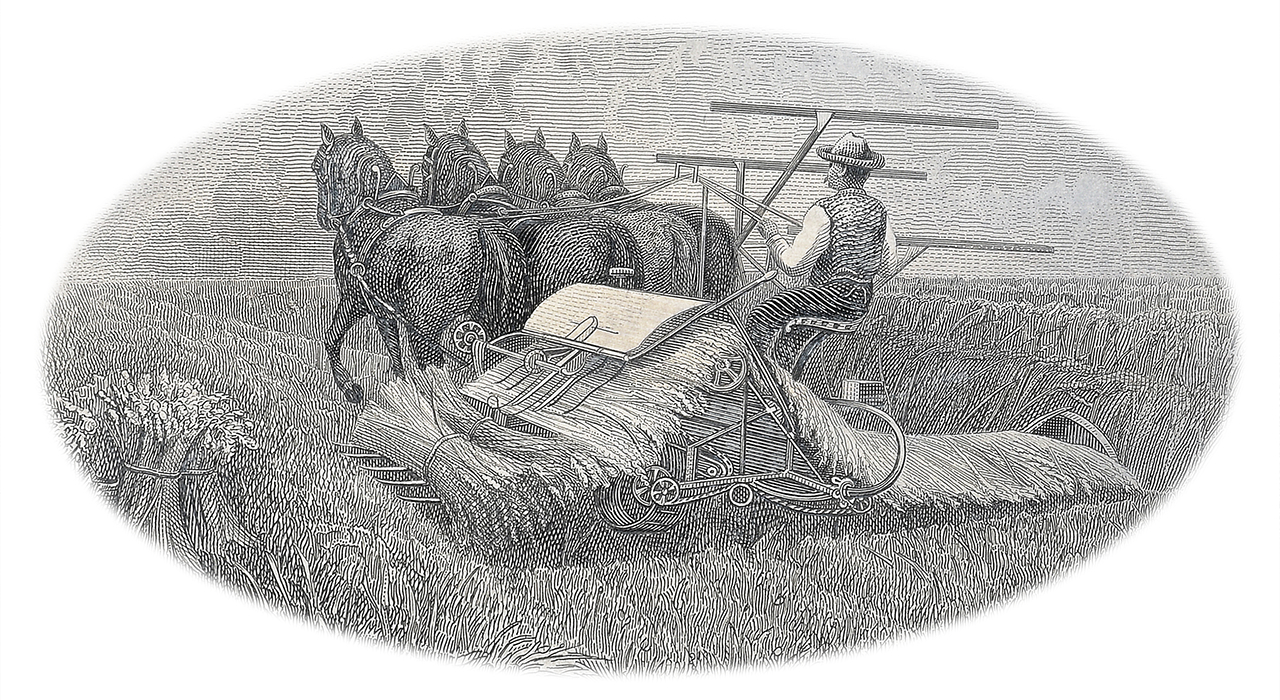
The Northern Crown Bank, $10, 1908. The use of this farming vignette on the bank note emphasizes the importance of this economic sector in early 20th century Canada. (NCC 1975.13.3)
The Museum Blog
Speculating on the piggy bank
By: Graham Iddon
New acquisitions—2024 edition
Money’s metaphors
Treaties, money and art
Rai: big money
By: Graham Iddon
Lessons from the Great Depression
By: Graham Iddon
Welcoming Newfoundland to Canada
By: David Bergeron
New Acquisitions—2023 Edition
Mo’ money, mo’ questions
Understanding cryptocurrencies
By: Graham Iddon














